Audience
This course is suitable for Cloud architects, administrators, and those working in SysOps/DevOps. Individuals using Google Cloud Platform to create new solutions or to integrate existing systems, application environments, and infrastructure with the Google Cloud Platform will also benefit from this course with a focus on Compute Engine
• Systems operations experience, including deploying and managing applications, either on-premises or in a public cloud environment
• Executives and business decision makers evaluating the potential of Google Cloud Platform to address their business needs
• Creating and maintaining machine learning and statistical models
• Querying datasets, visualizing query results and creating reports
Prerequisites
To get the most out of this course, you should have:
• Completed the Google Cloud Platform Fundamentals or have equivalent experience
• Basic proficiency with command-line tools and Linux operating system environments
Skills Gained
To get the most out of this course, you should have:
• Understand the purpose of and use cases for the products and services in the Google Cloud big data and machine learning platforms
• Explain how software containers work and the architecture of Kubernetes
• Understand how pod networking works in Kubernetes Engine
• Create and manage Kubernetes Engine clusters using the GCP Console and gcloud/ kubectl commands
• Launch, roll back and expose jobs in Kubernetes
• Manage access control using Kubernetes RBAC and Google Cloud IAM
• Manage pod security policies and network policies
• Use Secrets and ConfigMaps to isolate security credentials and configuration artifacts
• Understand GCP choices for managed storage services
• Monitor applications running in Kubernetes Engine
Course outline
Module 1: Introduction to Google Cloud Platform
• The Google Cloud Platform Console
• Cloud Shell
• Define cloud computing
• Identify GCPs compute services
• Regions and zones
• The cloud resource hierarchy
• Administer your GCP resources
Module 2: Containers and Kubernetes in GCP
• Create a container using Cloud Build
• Store a container in Container Registry
• The relationship between Kubernetes and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
• How to choose among GCP compute platforms
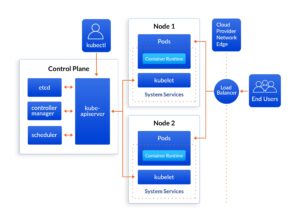
Module 3: Kubernetes Architecture
• The architecture of Kubernetes: pods, namespaces
• The control-plane components of Kubernetes
• Create container images using Google Cloud Build
• Store container images in Google Container Registry
• Create a Kubernetes Engine cluster
Module 4: Kubernetes Operations
• Work with the kubectl command
• Inspect the cluster and Pods
• View a Pods console output
• Sign in to a Pod interactively
Module 5: Deployments, Jobs, and Scaling
• Create and use Deployments
• Create and run Jobs and CronJobs
• Scale clusters manually and automatically
• Configure Node and Pod affinity
• Get software into your cluster with Helm charts and Kubernetes Marketplace
Module 6: GKE Networking
• Create Services to expose applications that are running within Pods
• Use load balancers to expose Services to external clients
• Create Ingress resources for HTTP(S) load balancing
• Leverage container-native load balancing to improve Pod load balancing
• Define Kubernetes network policies to allow and block traffic to pods
Module 7: Persistent Data and Storage
• Use Secrets to isolate security credentials
• Use ConfigMaps to isolate configuration artifacts
• Push out and roll back updates to Secrets and ConfigMaps
• Configure Persistent Storage Volumes for Kubernetes Pods
• Use StatefulSets to ensure that claims on persistent storage volumes persist across restarts
Module 8: Access Control and Security in Kubernetes and Kubernetes Engine
• Kubernetes authentication and authorization
• Kubernetes RBAC roles and role bindings for accessing resources in namespaces
• Kubernetes RBAC cluster roles and cluster role bindings for accessing cluster-scoped resources
• Define Kubernetes pod security policies
• The structure of GCP IAM
• IAM roles and policies for Kubernetes Engine cluster administration
Module 9: Logging and Monitoring
• Use Stackdriver to monitor and manage availability and performance
• Locate and inspect Kubernetes logs
• Create probes for wellness checks on live applications
Module 10: Using GCP Managed Storage Services from Kubernetes Applications
• Pros and cons for using a managed storage service versus self-managed containerized storage
• Enable applications running in GKE to access GCP storage services
• Use cases for Cloud Storage, Cloud SQL, Cloud Spanner, Cloud Bigtable, Cloud Firestore, and BigQuery from within a Kubernetes application
Schedule
Click on the following link to see the current Course Schedule
Our minimum class-size is 3 for this course.
If there are no scheduled dates for this course, it can be customized to suit the time and skill needs of clients and it can be held online, at a rented location or at your premises.
Click on the following link below to arrange for a custom course: Enquire about a course date







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.